GASCONTEC Technology solutions for Low-Carbon Hydrogen, Ammonia and Methanol solutions.

GasConTec stands for Gas Conversion Technologies.
We are a NEXTCHEM’s company registered in Bad Homburg, Germany, with a focus on technology solutions and more than 80 patents for the production of hydrogen, ammonia and methanol with very low CO2 carbon footprint in the production process.
Our technology solutions portfolio allows us to unique and climate positive investment in advanced methanol, hydrogen & ammonia production technologies. NEXTCHEM offers license, process design package (PDP), proprietary equipment (PEQ), training, digital & post-PDP services.
Relying on hundreds of years of experience and expertise of our team members, GasConTec offers a unique combination of innovation, brain power and experience.

NX AdWinHydrogen® Suite
In today’s scenario, hydrogen is key lever to decarbonize different industrial sectors: transports, hard-to-abate industries (such as steel production and cement) and fertilizers. In this context, low carbon H2 acts both as energy vector and chemical building block contributing in a multitude of industrial applications.

The most efficient way to produce Low Carbon Hydrogen
NX AdWinHydrogen® Suite technology is applied for converting hydrocarbon (C1 to C6) into hydrogen. This technology leverages an autothermal reformer operating at high pressure (60+ bar) for producing hydrogen.
NX AdWinHydrogen® Suite is best designed for production of Blue Hydrogen, Blue ammonia and Low Carbon Methanol.

Key features
High operating pressure reduces Capex (ca. 10% lower vs other top players) and higher energy efficiency
Flexible feedstock intake from C1 to heavier hydrocarbons (up to C6)
Robust and proven equipment integrated in a well-established syngas production unit
NX AdWinMethanol® Suite
Methanol is anticipated to play a pivotal role in advancing the energy transition across diverse sectors. It is expected to serve as a crucial energy carrier for decarbonizing the maritime transport sector and, through the production of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), also the aviation sector.
Additionally, methanol is well-known for being a key intermediate for producing polyolefins via the MTO process or gasoline through the DME route.
Hence, this versatile molecule will be an important building block of a new sustainable industrial chemistry.

Our solution for sustainable Methanol
NX AdWinMethanol® Suite technology relies on well-established isothermal catalytic reactors for producing methanol using syngas or CO2 and H2 as feedstocks for any specific methanol product quality (e.g., Grade AA). NX AdWinMethanol® Suite can be combined with NX AdWinHydrogen® Suite or with electrolyzers to produce methanol at reduced carbon footprint.

Key features
Suitable for large scale plants
Scalable technology for the development of small-scale optimized methanol plants (200-600 tpd)
Flexible technology for designing different methanol production routes with various carbon footprint
We have projects in the USA, South America, Mexico, Africa, Egypt, China and the Middle East with clients and partners like Mexinol and OCI.
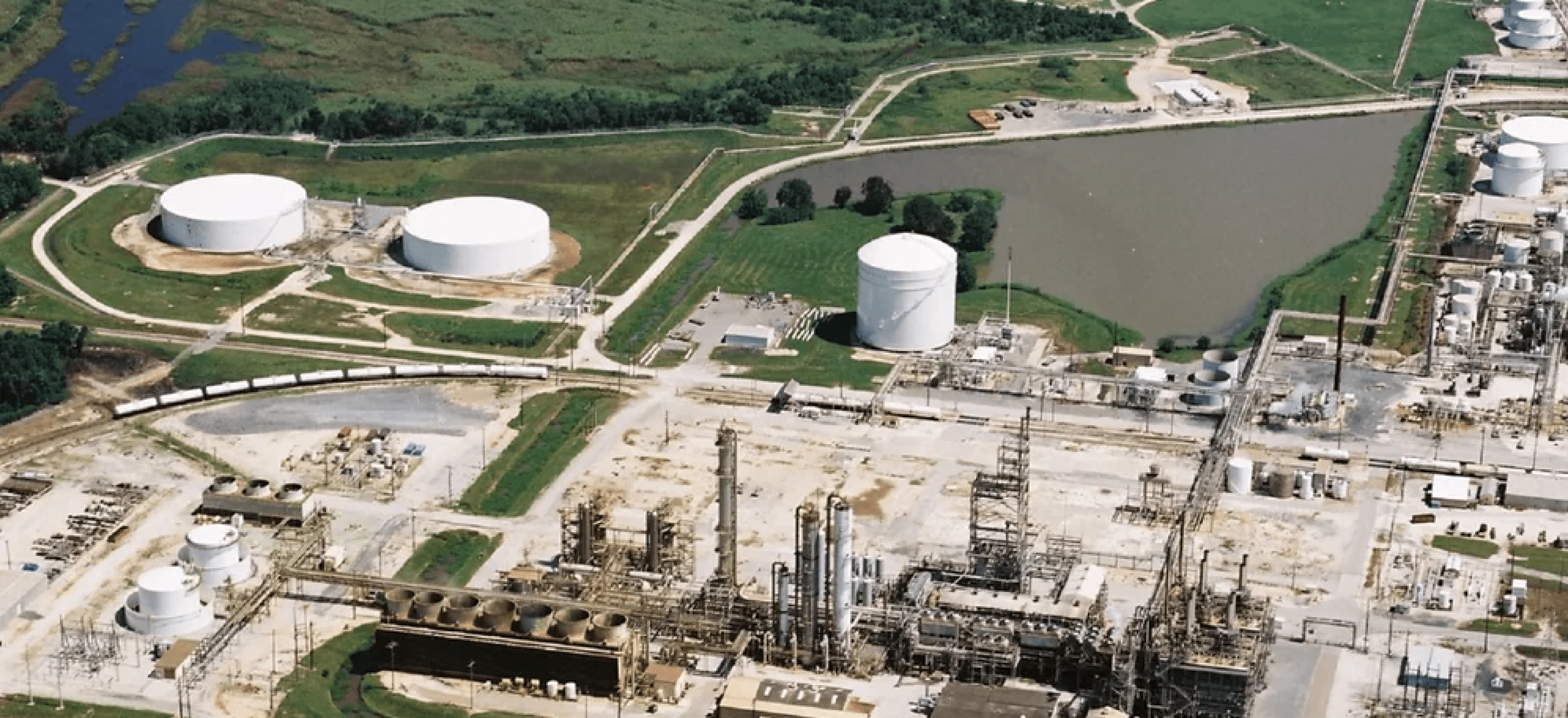
DELIVERED PROJECTS
Firewater Methanol Project, Beaumont, Texas, USA
Development of a 1,700,000 t/a methanol project;
2013-2015. Technology advisor and owner's engineer; 2015-2018
OCI Beaumont, Texas, USA
Plant revamp and start-up; sale of shares; 2011 - 2014
ONGOING PROJECT
Mexinol
Pacífico Mexinol project, a 6,145 Metric Tons (MT) per day methanol production facility in Sinaloa, Mexico.
When it initiates operations, Pacifico Mexinol is expected to be the largest single ultra-low carbon chemicals facility in the world, producing approximately 300,000 MT of green methanol from captured carbon and green hydrogen and 1.8 million MT of blue methanol per year from natural gas with carbon capture.
The methanol production plant will use GasConTec’s (GCT) NX- AdWinMethanol® technology and GasConTec’s (GCT) NX- AdWinMethanol Zero® technology, which together are considered the most advanced in terms of carbon conversion & energy use, and in addition to this, have the best environmental performance when compared to any other technology used for methanol production worldwide, eliminating almost entirely, GHGs emissions.